Gas and heat dynamics of a micro-scaled atmospheric pressure plasma reference jet. Kelly, S; Golda, J; Turner, M.M; Schulz-Von Der Gathen, V. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics 2015
Plasmas are exploited for applications in biomedicine, for example in sterilisation, tackling antimicrobial resistance and new cancer therapeutics.
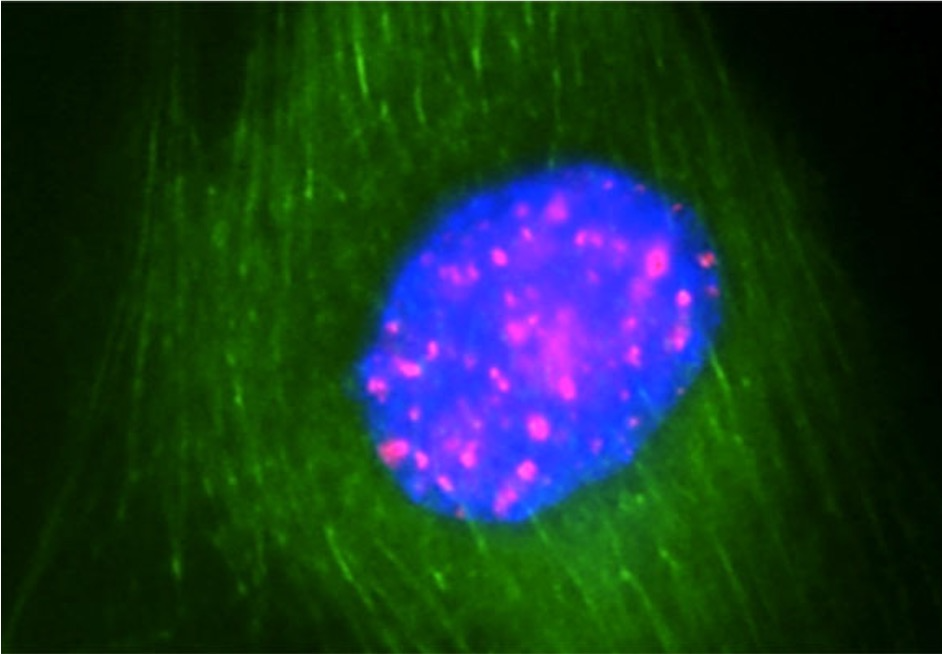
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/6894576: A.M. Hirst et al. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 42(10) 2740 (2004) doi: 10.1109/TPS.2014.2351453.
About the Research Area
The main motivation of LTPS for biomedical applications stems from their ability to generate and deliver reactive atomic and molecular species (both long- and short-lived), along with other active components such as UV, charged particles, and electric fields, under ambient conditions to a target. LTPs can stimulate specific biological responses, this is not only, but at least significantly due to the fact that low temperature plasma generated Reactive Oxygen Nitrogen Species (RONS) are the same as the RONS produced endogenously in the human body. They mediate many physiological processes, such as cell-to-cell signalling, immune response, wound healing and cell death processes, so therefore the plasma produced species are expected to mimic the functions of their native counterparts. Many existing clinical therapies already rely on these. The advantage of LTPs is that they directly and simultaneously produce these components offering unique synergies capable of stimulating specific biological responses. Our research involves understanding the plasma driven mechanisms of action and engineering controllable plasma delivery strategies.
Biomedical Plasmas Publications
What is the best method? Recovery of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli from inanimate hospital surfaces. Claro, T; Galvin, S; Cahill, O; Fitzgerald-Hughes, D; Daniels, S; Humphreys, H. Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology 2014
Fragmentation of neutral amino acids and small peptides by intense, femtosecond laser pulses. Duffy, M.J; Kelly, O; Calvert, C.R; King, R.B; Belshaw, L; Kelly, T.J; Costello, J.T; Timson, D.J; Bryan, W.A; Kierspel, T; Turcu, I.C.E; Cacho, C.M; Springate, E; Williams, I.D; Greenwood, J.B. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry 2013