Abstract
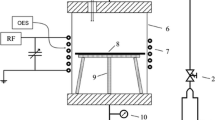
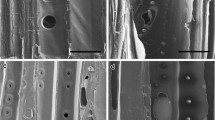
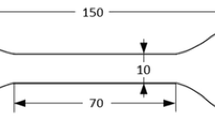
Low temperature plasma process is an effective alternative method compared to the conventional vacuum drying method for removing moisture. Plasma drying removes the moisture from fibres faster and to a lower level than conventional methods. It also improves the surface properties of the fibres. The jute fibre was treated with inert gas argon plasma without damaging the fibre. The OES was used to monitor the moisture desorbed from the fibre during processing. The XRD results revealed a change in the macromolecular structure as well as the crystallinity of the treated fibre. The FTIR and TGA provided the evidence of moisture removal from the fibres. It was found that the plasma treated fibres contain less than 1.8% (wt.) moisture which is a promising result when compared with conventional drying processes.The average tensile strength of the plasma treated fibres increased by 12.5% compared with those treated with the conventional vacuum dry process.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hua ZQ, Sitaru R, Denes F (1997) Plasma Polym 2(3):199
Oraji R (2008) The effect of plasma treatment on flax fibres, [M Eng Thesis]. Department of Agriculture and Bioresource Engity University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon
Misra S, Mohanty A (2003) Compos Sci Technol 63:1377
Bellmann C, Caspari A, Albrecht V et al (2005) Surf A Physicochem Eng Aspects 267:19
Santulli C, Caruso AP (2009) J Malays Polym 4:19
Bavan DS, Kumar GCM (2010) J Reinforc Plast Compos 29(24):3600
Cullity BD, Stock SR (2001) Elements of X-ray diffraction, 3rd edn. Prentice-Hall, New Jersey
Morshed MM, Alam MM, Daniels SM (2010) Plasma Sci Technol 12:325
Roy G, Saha SC (2011) Ind J Fibr Textl Res 36:178
Hosomi K, Kikawa T, Goto S, Yamada H, Katsuyama T, Arakawa Y (2006) J Vac Sci Technol B24:1226
Xiong Q, Nikiforov AY, Lu XP, Leys C (2010) J Phys D Appl Phys 43:415201
Socrates G (2001) Infrared and Raman characteristic group frequencies, 3rd edn. Wiley, West Sussex
Sarani A, Nikiforov AY, Leys C (2010) Phys Plasm 17:063504
Spinace MAS, Labert CS, Frmoselli KKG, De Paoli Macro A (2009) Carbohydr Polym 77:47
Ray D, Sarkar BK, Basak RK, Rana AK (2002) J Appl Polym Sci 85:2594
Acknowledgments
The author would like to thanks Mr Mir Mohammad Faruk and Mr Mohiuddin Patoary who have supplied the environment friendly natural fibre from Bangladesh. The author also would like to thank the NCPST for use of their facilities for plasma treatment and characterization.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morshed, M.M., Alam, M.M. & Daniels, S.M. Moisture Removal from Natural Jute Fibre by Plasma Drying Process. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 32, 249–258 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-011-9340-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-011-9340-1