Abstract
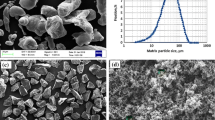
Due to the difficulty of preparation and beneficial properties achievable, copper and iron matrix nanocomposites are materials for which fabrication via the powder metallurgy route is attracting increasing research interest. The presence of ceramic nanoparticles in their matrix can lead to considerable changes in the microstructure and morphology. The effects of the type of metallic matrix and ceramic nanoparticle on the distribution of nano reinforcements and the morphology of ball-milled composite powders were evaluated in this study. For this purpose, 25 wt % of Al2O3 and SiC nanoparticles were separately ball-milled in the presence of iron and copper metals. The SEM, FESEM, and XRD results indicated that as-received nanoparticles, which were agglomerated before milling, were partially separated and embedded in the matrix of both the metals after the initial stages of ball milling, while prolonged milling was not found to further affect the distribution of nanoparticles. It was also observed that the Al2O3 phase was not thermodynamically stable during ball milling with copper powders. Finally, it was found that the presence of nanoparticles considerably reduce the average size of metallic powder particles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Valibeygloo, R. A. Khosroshahi, and R. T. Mousavian, “Microstructural and mechanical properties of Al–4.5 wt % Cu reinforced with alumina nanoparticles by stir casting method,” Int. J. Miner., Metall., Mater., 20, 978–985 (2013).
A. F. Boostani, S. Tahamtan, Z. Y. Jiang, D. Wei, S. Yazdani, R. A. Khosroshahi, R. T. Mousavian, J. Xu, X. Zhang, and D. Gong, “Enhanced tensile properties of aluminum matrix composites reinforced with graphene encapsulated SiC nanoparticles,” Composites Part A: Appl. Sci. Manufact., 68, 155–163 (2015).
G. Mojtaba, M. S. Morteza, T. Majid, K. R. Jalal, and T. Reza, “Modification of stone matrix asphalt with nano-SiO2,” J. Basic Appl. Sci. Res. 2, 1338–1344 (2012).
A. F. Boostani, S. Yazdani, R. T. Mousavian, S. Tahamtan, R. A. Khosroshahi, and D. Wei, “Strengthening mechanisms of graphene sheets in aluminum matrix nanocomposites,” Mater. Design 88, 983–989 (2015).
R. T. Mousavian, R. A. Khosroshahi, S. Yazdani, D. Brabazon, and A. F. Boostani, “Fabrication of aluminum matrix composites reinforced with nano- to micrometer-sized SiC particles,” Mater. Design 89, 58–70 (2016).
D. Miracle, “Metal matrix composites–from science to technological significance,” Composites Sci. Technol. 65, 2526–2540 (2005).
R. F. Gibson, “A review of recent research on mechanics of multifunctional composite materials and structures,” Compos. Struct. 92, 2793–2810 (2010).
F. Toptan, A. Kilicarslan, A. Karaaslan, M. Cigdem, and I. Kerti, “Processing and microstructural characterisation of AA 1070 and AA 6063 matrix B4Cp reinforced composites,” Mater. Design 31, S87–S91 (2010).
M. Forouzan, R. T. Mousavian, T. Sharif, and Y. Afkham, “A three-step synthesis process of submicron boron carbide powders using microwave energy,” J. Thermal Anal. Calorim. 122, 579–588, (2015).
K. A. Nekouee, R. Khosroshahi, R. T. Mousavian, and N. Ehsani, “Sintering behavior and microwave dielectric properties of SiO2–MgO–Al2O3–TiO2 ceramics,” J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron., 27, 3570–3575 (2016).
R. T. Mousavian, N. Azizi, Z. Jiang, and A. F. Boostani, “Effect of Fe2O3 as an accelerator on the reaction mechanism of Al–TiO2 nanothermite system,” J. Thermal Anal. Calorim. 117, 711–719 (2014).
A. Mosleh, M. Ehteshamzadeh, and R. T. Mousavian, “Fabrication of an r-Al2Ti intermetallic matrix composite reinforced with a-Al2O3 ceramic by discontinuous mechanical milling for thermite reaction,” Int. J. Miner., Metall., Mater. 21, 1037–1043 (2014).
R. T. Mousavian, S. Sharafi, and M. Shariat, “Preparation of nano-structural Al2O3–TiB2 in-situ composite using mechanically activated combustion synthesis followed byintensive milling,” Iran. J. Mater. Sci. Eng. 8, 1–9 (2011).
R. T. Mousavian, S. Sharafi, M. Roshan, and M. Shariat, “Effect of mechanical activation of reagents’ mixture on the high-temperature synthesis of Al2O3–TiB2 composite powder,” J. Therm. Anal. Calor. 104, 1063–1070 (2011).
R. T. Mousavian, S. Sharafi, and M. Shariat, “Microwave- assisted combustion synthesis in a mechanically activated Al–TiO2–H3BO3 system,” Int. J. Refract. Metals and Hard Mater. 29, 281–288 (2011).
C. Suryanarayana, “Mechanical alloying and milling,” Progress Mater. Sci. 46, 1–184 (2001).
S. Romankov, S. Komarov, E. Vdovichenko, Y. Hayasaka, N. Hayashi, S. Kaloshkin, and E. Kasai, “Fabrication of TiN coatings using mechanical milling techniques,” Int. J. Refract. Metals Hard Mater. 27, 492–497 (2009).
M. Zawrah, H. A. Zayed, R. A. Essawy, A. H. Nassar, and M. A. Taha, “Preparation by mechanical alloying, characterization and sintering of Cu–20 wt % Al2O3 nanocomposites,” Mater. Design 46, 485–490 (2013).
C. Suryanarayana and N. Al-Aqeeli, “Mechanically alloyed nanocomposites,” Progress Mater. Sci. 58, 383–502 (2013).
S. Sulaiman, M. Sayuti, and R. Samin, “Mechanical properties of the as-cast quartz particulate reinforced LM6 alloy matrix composites,” J. Mater. Proc. Technol. 201, 731–735 (2008).
A. Pramanik and G. Littlefair, “Fabrication of nanoparticle reinforced metal matrix composites,” Adv. Mater. Res. 651, 289–294 (2013).
P. Mohanty, K. Mishra, R. Bosu, and P. Padhi, “Achieving uniform nanoparticle distributions of bulk Al/Al2O3 metal matrix nanocomposites,” Int. J. Nanomanufact. 10, 478–488 (2014).
A. F. Boostani, Z. Y. Jiang, R. T. Mousavian, S. Tahamtan, S. Yazdani, R. A. Khosroshahi, J. Z. Xu, D. Gong, X. M. Zhang, and D. Wei, “Graphene sheets encapsulating SiC nanoparticles: A roadmap towards enhancing tensile ductility of metal matrix composites,” Mater. Sci. Eng., A 648, 92–103 (2015).
A. F. Boostani, R. T. Mousavian, S. Tahamtan, S. Yazdani, R. A. Khosroshahi, D. Wei, J. Xu, X. Zhang, and Z.Y. Jiang, “Solvothermal-assisted graphene encapsulation of SiC nanoparticles: A new horizon toward toughening aluminum matrix nanocomposites,” Mater. Sci. Eng., A 653, 99–107 (2016).
R. T. Mousavian, R. A. Khosroshahi, S. Yazdani, and D. Brabazon, “Manufacturing of cast A356 matrix composite reinforced with nano- to micrometer-sized SiC particles,” Rare Metals, 36, 46–54 (2017).
S. Bernoosi, R. A. Khosroshahi, and R. T. Mousavian, “Mechanical properties of hot-pressed Al–4.5 wt % Cu/WC composite,” J.Ultrafine Grained and Nanostruct. Mater. 47, 63–70 (2014).
I. Ozdemir, S. Ahrens, S. Mücklich, and B. Wielage, “Nanocrystalline Al–Al2O3p and SiCp composites pro duced by high-energy ball milling,” J. Mater. Proc. Technol. 205, 111–118 (2008).
S. R. Tousi, R. Y. Rad, E. Salahi, I. Mobasherpour, and M. Razavi, “Production of Al–20 wt % Al2O3 composite powder using high energy milling,” Powder Technol. 192, 346–351 (2009).
M. Phasha, K. Maweja, and C. Babst, “Mechanical alloying by ball milling of Ti and Mg elemental powders: Operation condition considerations,” J. Alloys Compd. 492, 201–207 (2010).
H. Zhou, L. Hu, H. Sun, and X. Chen, “Synthesis of nanocrystalline Mg-based Mg–Ti composite powders by mechanical milling,” Mater. Charact. 106, 44–51 (2015).
M. Alizadeh and M. M. Aliabadi, “Synthesis behavior of nanocrystalline Al–Al2O3 composite during low time mechanical milling process,” J. Alloys Compd. 509, 4978–4986 (2011).
H. Ahamed and V. Senthilkumar, “Role of nano-size reinforcement and milling on the synthesis of nanocrystalline aluminum alloy composites by mechanical alloying,” J. Alloys Compd. 505, 772–782 (2010).
E. Salahi and A. Rajabi, “Fabrication and characterisation of copper–alumina nanocomposites prepared by high-energy fast milling,” Mater. Sci. Technol. 32, 1212–1217 (2016).
M. Ramezani and T. Neitzert, “Mechanical milling of aluminum powder using planetary ball milling process,” J. Achiev. Mater. Manufact. Eng. 55, 790–798 (2012).
E. Nes, “Modelling of work hardening and stress saturation in fcc metals,” Prog. Mater. Sci. 41, 129–193 (1997).
S. Yi, K. Trumble, and D. Gaskell, “Thermodynamic analysis of aluminate stability in the eutectic bonding of copper with alumina,” Acta Mater. 47, 3221–3226 (1999).
M. A. Meyers, A. Mishra, and D. J. Benson, “Mechanical properties of nanocrystalline materials,” Prog. Mater. Sci. 51, 427–556 (2006).
M. A. Meyers and K. K. Chawla, Mechanical Behavior of Materials, (Cambr. Univ. Press, Cambridge, 2009), vol. 2.
P. le Brun, E. Gaffet, L. Froyen, and L. Delaey, “Structure and properties of Cu, Ni and Fe powders milled in a planetary ball mill,” Scr. Metall. Mater. 26, 1743–1748 (1992).
F. Zhou, X. Liao, Y. Zhu, S. Dallek, and E. Lavernia, “Microstructural evolution during recovery and recrystallization of a nanocrystalline Al–Mg alloy prepared by cryogenic ball milling,” Acta Mater. 51, 2777–2791 (2003).
D. Brabazon, D. Browne, and A. J. Carr, “Mechanical stir casting of aluminum alloys from the mushy state: Process, microstructure and mechanical properties,” Mater. Sci. Eng., A 326, 370–381 (2002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Russian in Fizika Metallov i Metallovedenie, 2017, Vol. 118, No. 8, pp. 790–800.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Afkham, Y., Khosroshahi, R.A., Kheirifard, R. et al. Microstructure and morphological study of ball-milled metal matrix nanocomposites. Phys. Metals Metallogr. 118, 749–758 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X17080026
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X17080026